Keeping the outlet valve closed during Centrifugal pumps operation introduces multiple technical risks.

Uncontrolled energy conversion and thermodynamic imbalance
- 1.1 Under the closed condition of the surge of medium temperature, almost all the input energy is converted into heat energy. The medium is unable to take away the heat, causing the temperature in the pump chamber to rise sharply. Continuous operation will induce vaporization of the medium, accelerating the carbonization of the sealing material
1.2 Seal system failure In the environment of high temperature and vaporization of the medium, the mechanical seal that relies on the lubrication and cooling of the medium will lead to its overheating failure – the mechanical seal will have dry friction and the seal face will be burned.
Abnormal mechanical stress
- 2.1 Axial force overrun The axial force of the closing valve is usually 1.5-5 times that of normal working conditions, and the thrust bearing load may reach or even exceed its bearing limit, resulting in the fragmentation of the bearing cage or the deformation of the cage
2.2 Vibration and fatigue damage The difference in thermal expansion caused by high temperature leads to thermal deformation or thermal stress, abnormal gap between the impeller and the pump housing, and the influence of unbalanced hydraulic load, which causes the dynamic balance of the rotor to be damaged, the vibration increases, and the parts are fatigue damaged.
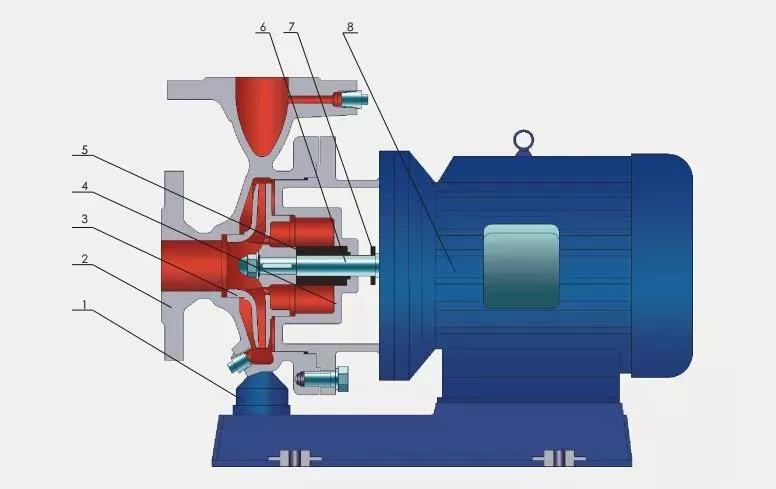
Cavitation and material damage
3.1 NPSH allowance inverted medium vaporization [make the cavitation allowance (NPSHa) of the device lower than the necessary NPSHr of the pump], forming bubbles, and the shock wave generated by the collapse of the bubbles can reach 690MPa, resulting in pitting and honeycomb spalling of the impeller runner
3.2 Metallographic structure deterioration For austenitic stainless steel impellers, sensitization may occur at local high temperatures, and the intergranular corrosion rate will increase and the tensile strength will decrease. For carbon steel impellers, the problems at high temperatures are more significant, such as high-temperature oxidation and decarburization, resulting in a decrease in surface strength and general policies; If it contains impurities such as sulfur and phosphorus, it is easy to segregate at grain boundaries at high temperatures, causing thermal brittleness and easy cracking during operation; Under long-term high temperature, carbon steel has poor creep resistance, and local high temperature may accelerate creep deformation, which will eventually lead to impeller fracture or fatigue failure.
System security and economic risks
4.1 The pressure of the pressure of the pressure bearing shell exceeds the limit and the operation of the closing valve makes the outlet pressure of the pump reach 120-150% of the rated value, and there is a risk of breaking through the set pressure of the safety valve, which may trigger pressure relief discharge or cracking of the pipeline weld
4.2 Energy consumption and maintenance costs surge Valve shutdown operation is the "killer condition" of centrifugal pumps, which significantly increases energy consumption in the short term, and long-term operation will lead to malignant damage to the equipment, and the comprehensive maintenance cost may increase by 3-10 times.
Deterioration of special media working conditions
For volatile media (e.g., LPG), the operation of the closed valve will accelerate the vaporization of the liquid phase, and the gas-liquid two-phase flow in the pump chamber will cause sudden flow changes, resulting in periodic oscillations of axial forces and accelerating the wear of components.
Industry experience and standard requirements
6.1 Industry experienceAccording to the actual engineering application experience, the running time limit of the centrifugal pump valve shall not exceed 2 minutes, and it is usually limited to 1 minute. It is recommended to set up an interlock control system to automatically trigger the shutdown protection program when the outlet valve closes and overtimes.
6.2 The standard specification requires that the API 610 12th Edition standard states that some high-energy, integrally geared or multistage pumps have a rapid temperature rise when the outlet valve is closed, which makes testing infeasible and/or unsafe when the valve is closed. Temperature rise is closely related to power density. Power density PD, which can be approximated as:
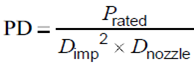
P rated: Power rating per stage when water in hp (or MW)
D imp: Rated impeller diameter in in. (or m)
D nozzle: Nominal outlet flange diameter in in. (or m). For double-suction, single-stage pumps, the D nozzle is the inlet flange diameter.
The typical critical value for PD is 0.286 hp/in.3 (13 MW/m3), beyond which it is recommended not to run the pump with the outlet valve closed during performance testing.
Post time: Jun-04-2025


